Understanding the Sand Casting Process
Sand casting is one of the oldest and most widely used metal casting processes. It involves the use of sand as the primary mold material, which is shaped to create a cavity that defines the desired geometric form of the final product. This process is highly versatile, adaptable for various metals, and widely utilized in industries from automotive to aerospace. This article explores the fundamental steps, advantages, and applications of the sand casting process.
Steps in the Sand Casting Process
1. Pattern Making The first step in sand casting is creating a pattern that is an exact replica of the object to be cast. Patterns can be made from wood, metal, or plastic and are typically slightly larger than the final object to accommodate for the shrinkage that occurs during the cooling of the metal.
2. Mold Preparation The pattern is placed in a mixture of sand and bonding agents, typically clay and water. The sand is packed tightly around the pattern to create a mold. Once the sand is compacted, the pattern is removed, leaving a cavity in the shape of the desired part. This process can be done in two halves (two-part molds) or as a single piece, depending on the complexity of the part.
3. Core Making For castings with internal cavities or complex shapes, cores made from sand are constructed. These cores are placed in the mold before the molten metal is poured in, allowing for the creation of internal features not achievable with the pattern alone.
4. Melting the Metal The chosen metal, usually aluminum, iron, or copper, is melted in a furnace. The molten metal must reach a specific temperature depending on the alloy composition, ensuring it flows easily into the mold.
5. Pouring Once the metal is molten, it is poured into the mold cavity. This step requires skill to ensure that the metal fills the mold completely without trapping air, which can lead to defects.
6. Cooling After pouring, the molten metal cools and solidifies within the mold. Cooling times depend on the metal type and the thickness of the casting.
what is sand casting process
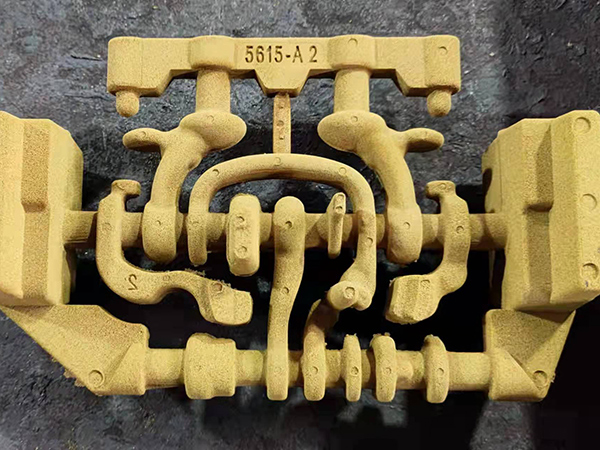
7. Mold Removal Once the casting has cooled sufficiently, the sand mold is broken away to reveal the metal casting. This is often done using mechanical vibration or by breaking the sand apart manually.
8. Finishing The final step includes cleaning and finishing the casting. This may involve sanding, grinding, or machining to meet the desired surface finish and dimensions.
Advantages of Sand Casting
Sand casting offers several benefits that make it a popular choice in manufacturing
- Cost-Effective The materials required for sand casting are relatively inexpensive, making it an economical choice for both small and large production runs. - Flexibility The process can accommodate a wide range of metal alloys and complex shapes, making it suitable for diverse applications. - Scalability From small prototypes to large-scale production, sand casting can be scaled to fit various manufacturing needs. - Complex Geometries It allows the creation of complex geometries that may be difficult to achieve with other methods.
Applications of Sand Casting
Sand casting is utilized across various industries. In the automotive sector, it is used to produce engine blocks, cylinder heads, and transmission cases. The aerospace industry relies on sand casting for components like turbine housings and structural components due to its ability to produce lightweight yet strong parts. Additionally, sand casting is also common in art and sculpture, where artists create intricate designs using this traditional method.
Conclusion
The sand casting process remains a cornerstone of metal manufacturing due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. Understanding this process provides insight into the fundamentals of metalworking and opens the door to numerous applications across various industries. As technology advances, so too does the sand casting process, continuously evolving to meet the ever-changing demands of modern manufacturing.
Post time:Eki . 16, 2024 10:11
Next:steel sand casting process
