- Introduction to critical importance of sand selection in foundry processes
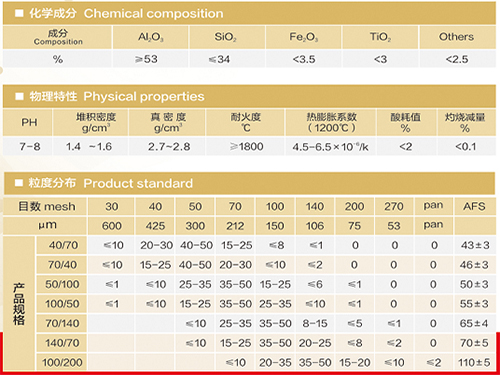
- Key parameters and performance data for foundry sands
- Technical advantages of primary foundry sand varieties
- Comparative analysis of leading foundry sand suppliers
- Customization strategies for specific casting applications
- Industry implementation case studies with measurable outcomes
- Future developments in foundry sand technology and selection criteria

(types of foundry sand)
Types of Foundry Sand: Foundational Elements of Metal Casting
Foundry sands constitute the essential molding medium enabling complex metal casting operations across industries. Approximately 70% of all metal castings produced globally depend critically on proper sand selection, influencing everything from dimensional accuracy to defect rates. Modern foundries utilize diverse sand formulations, each exhibiting distinct physical and thermal properties optimized for specific applications. The fundamental types include silica sands (quartz), chromite sands, zircon sands, olivine sands, and specialized synthetic varieties. Understanding these materials' characteristics remains paramount for achieving tight-tolerance castings with minimized surface imperfections and reduced rework rates.
Performance Characteristics and Material Specifications
Foundry sand effectiveness hinges on measurable parameters including permeability, refractoriness, thermal stability, and bonding characteristics. Current industry testing standards reveal significant differences:
• Permeability: Silica sands average 120-180 AFS units versus zircon's 50-70 units, directly impacting gas venting capabilities
• Thermal expansion: Zircon demonstrates minimal 0.8% expansion compared to silica's problematic 1.5-2.0%
• Heat transfer: Chromite's density (4.7g/cm³) enables 15-20% faster cooling than typical silica
According to Foundry Management & Technology reports, consistent grain size distribution between 60-220 AFS governs strength uniformity, while clay content below 2% prevents excessive moisture retention. Crucially, modern foundries utilize sands with pH values between 6.5-8.0 to ensure chemical compatibility with both ferrous and non-ferrous alloys.
Technical Properties of Primary Sand Varieties
Each sand type delivers unique metallurgical advantages:
Silica sands dominate 57% of the global foundry sand market (IMA-Europe 2023) due to cost-effectiveness and excellent flowability. However, limitations include cristobalite formation during repeated heating cycles, gradually degrading performance after eight reclamation cycles.
Zircon sands exhibit superior thermal properties, with refractoriness exceeding 2200°C. This enables exceptional dimensional stability for high-precision aerospace components, reducing finishing operations by 30-45%. The high zirconium silicate content (≥67%) minimizes metal penetration defects in thin-section castings.
Chromite sands provide unparalleled thermal conductivity, accelerating solidification rates and enabling production cycle reductions up to 25% for automotive part manufacturing. Their natural resistance to slag erosion significantly extends mold life during heavy steel casting.
Supplier Capabilities Comparison
| Supplier | Core Products | Global Capacity | Specialized Offerings | Reclamation Tech |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vesuvius Foundry | Zircon, Chromite, Ceramic Sands | 950,000 MT/year | Low-Zr alternatives | Thermal-mechanical hybrid |
| Höganäs Borgestad | Silica, Olivine Systems | 1.2M MT/year | Pre-coated bonding systems | Dry attrition systems |
| Elkem Materials | Specialty Sands, Recycled Silica | 700,000 MT/year | Alumina-silicate blends | Closed-loop water systems |
Application-Based Material Customization
Progressive foundries deploy sand-specific formulations matching operational requirements:
High-chrome steel casting: Multi-layer molds combining chromite facing sands with silica backup sands reduce penetration defects by 40% while cutting material costs 15%
Aluminum permanent mold: Synthetic ceramic sands (85% alumina / 15% silica) achieve near-net-shape capability (±0.25mm tolerance), decreasing machining requirements by 55%
Rapid prototyping: 3D-printed molds using Furfuryl alcohol-bonded zircon sands enable lead time reductions from weeks to 48 hours for complex geometries
Industrial Implementation Case Studies
Automotive transmission case production: A Tier-1 supplier transitioned to fused silica blends for core manufacturing, achieving:
• 21% reduction in gas-related porosity defects
• 15% decrease in shot blasting time
• Core usage efficiency improvement from 5.2 to 8.3 cycles
Marine valve body foundry: Implementation of zircon-chromite composite molds reduced dimensional variability from ±1.8mm to ±0.5mm while decreasing scrap rates from 8.2% to 3.1%
Advancements in Types of Foundry Sand Applications
Emerging developments promise transformative effects on foundry sand applications within the next five years. Nano-engineered coatings now enhance sand thermal performance without altering base material parameters - initial trials demonstrate 17% higher heat dissipation in silica sands treated with zirconia nanoparticles. Sustainable formulations incorporating industrial waste streams (coal fly ash, slag derivatives) simultaneously deliver 15-20% material cost reductions while maintaining metallurgical properties. Global standardization initiatives like ISO 26845-2024 provide quantifiable classifications for sand performance attributes, creating consistent benchmarks for selecting optimal sand types across different metal casting scenarios.
(types of foundry sand)
FAQS on types of foundry sand
Q: What are the main types of foundry sand used in metal casting?
A: The primary types include green sand, resin sand, water glass (sodium silicate) sand, and ceramic sand. Each offers unique properties like cost efficiency, mold strength, or heat resistance for different casting needs. Specialty sands like zircon and chromite are also used for specific high-precision applications.
Q: How do types of sand in foundry operations vary based on binder materials?
A: Foundry sands are categorized by binders: clay-bonded (green sand), synthetic resins (phenolic or furan), inorganic binders (sodium silicate), or no-binder ceramic variants. Binders determine characteristics like collapsibility, reusability, and curing speed. This directly impacts mold durability and casting surface finish.
Q: What distinguishes green sand from other types of foundry sand?
A: Green sand contains natural clay, water, and silica sand without baking, making it reusable and cost-effective. Unlike resin sands requiring chemical catalysts, it maintains moisture for plasticity during molding. However, it offers lower dimensional accuracy than synthetic binder systems.
Q: Why are different types of foundry sand chosen for specific casting applications?
A: Selection depends on factors like metal pouring temperature, part complexity, and tolerance requirements. For example, zircon sand handles high-temperature alloys, while resin sand ensures precision for intricate cores. Economics and environmental factors also drive choices like reclaimed sand usage.
Q: Which types of foundry sand provide the best surface finish for castings?
A: Fine-grained sands like zircon or resin-bonded variants yield superior surface finishes. Their tight grain structure minimizes metal penetration into molds, reducing surface defects. Ceramic sands also excel in finish quality for investment casting applications.
Next:Furan Resin Sand Casting - High Precision & Efficiency Solutions
